All NVIDIA GPUs starting with Kepler support fully-accelerated hardware video encoding; GPUs starting with Fermi support fully-accelerated hardware video decoding. The recently released Turing hardware delivered Tensor Cores and better machine learning performance, but the new GPU also incorporated new multimedia features such as an improved NVENC unit to deliver better compression and image quality in video codecs.
Let’s take a closer look at performance and quality of the new NVENC unit designed into Turing.
NVENC Performance Test Setup
H.264 emerged 15 years ago and has become an ubiquitous video coding standard. It has become most important and widespread codec in the industry. These tests show how the Tesla T4 performs versus the well-known open source encoder libx264 in two scenarios:
- High Quality mode which represents most common encoding scenarios with VBR control and B frames enables.
- Low Latency Fast mode which is useful in applications sensible to latency such as remote gaming or video conferencing.
For that, testing computer was prepared with the configuration shown in table 1:
| Component | Tesla T4 NVENC | libx264 |
| CPU | Dual Intel Xeon E5-2660v3 @ 2.6 GHz | Dual Intel Xeon E5-2660v3 @ 2.6 GHz |
| GPU | TU104 (Tesla T4) | N/A |
| RAM | 128 GB | 128 GB |
| FFMPEG | 4.0.2 | 4.0.2 |
| Driver | 415.15 | N/A |
These performance tests set the encode parameters to those shown in table 2:
| Preset | NVENC | libx264 |
| High Quality | -c:v h264_nvenc -preset medium -b:v BITRATE -bufsize BITRATE*2 -profile:v high -bf 3 -b_ref_mode 2 -temporal-aq 1 -rc-lookahead 20 -vsync 0 | -c:v libx264 -preset medium -b:v BITRATE -bufsize BITRATE*2 -profile:v high -tune psnr -vsync 0 -threads 4 |
| Low Latency Fast | -c:v h264_nvenc -preset llhp -rc cbr_ld_hq -b:v BITRATE -bufsize BITRATE/FRATE -profile:v high -g 999999 -vsync 0 | -c:v libx264 -preset fast -b:v BITRATE -bufsize BITRATE/FRATE -profile:v high -g 999999 -x264opts no-sliced-threads:nal-hrd=cbr -tune zerolatency -threads 4 -vsync 0 |
We used a variety of input videos for RD-estimation, such as basketball_drive, bq_terrace, cactus, crowd_run, ducks_take_off, jokey, kimono, and many more at 1280×720, 1920×1080 and 3840×2160 resolutions.
Performance and Quality Results
Balanced Sequences
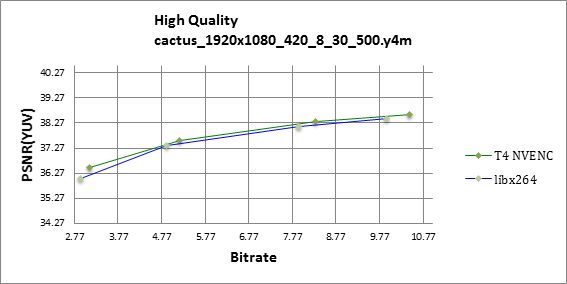
Figures 1 through 4 show that the Tesla T4 delivers same or slightly better visual quality to libx264 in high quality mode for all-round balanced sequences like Kimono, BQ terrrace and Park Scene.
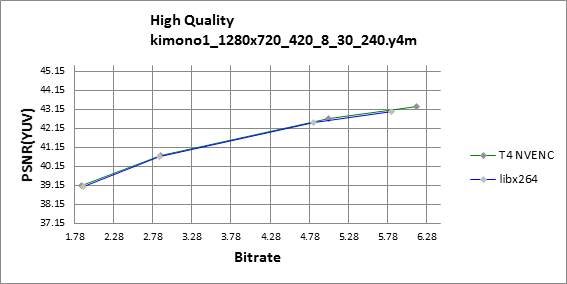
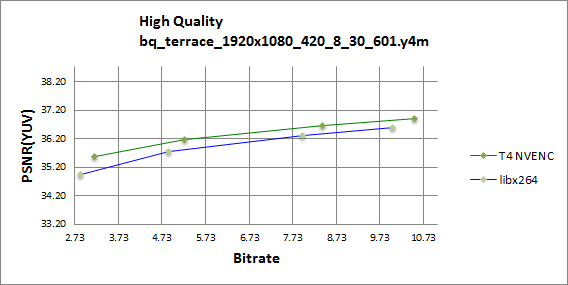
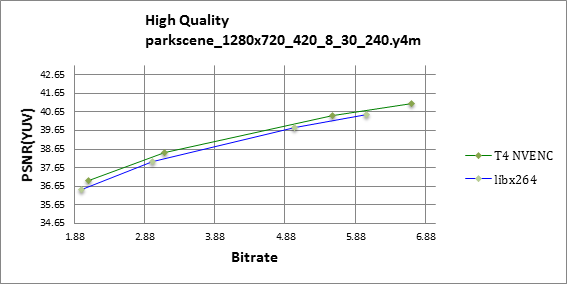
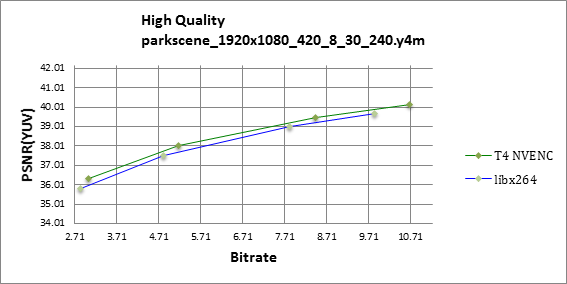
Tesla T4 shows better prediction and filtering in comparison to libx264, as illustrated on figures 5 and 6.


High-Motion Sequences
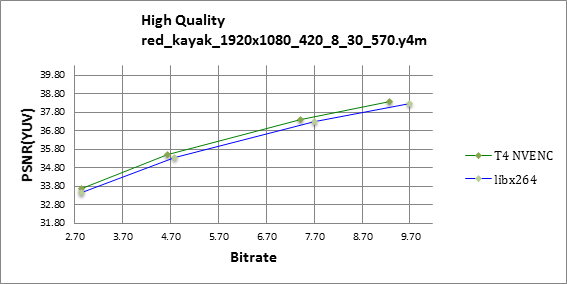
The Red Kayak and Cactus sequences include significant chaotic and circular motion, respectively. NVENC shows a clear advantage over libx264 in these scenes which contain complex inter-predicition, as shown on figures 7 and 8.
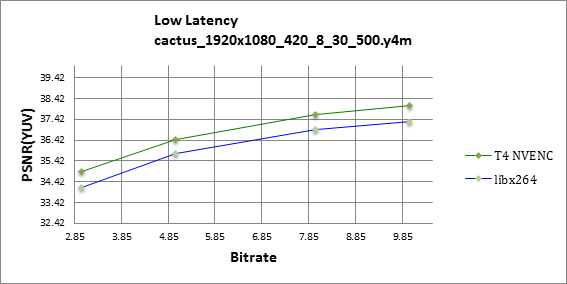
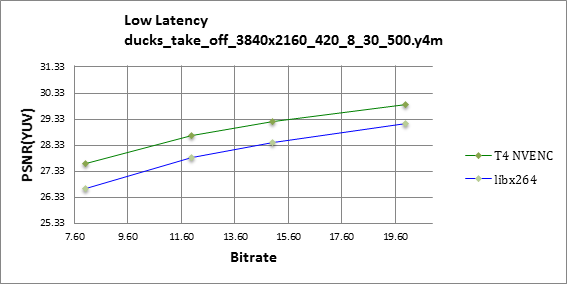
The Tesla T4 NVENC easily outperforms libx264 in low-latency mode as highlighted in figures 9 and 10. Notice how the Tesla T4 is more effective at high resolutions, offering one dB better visual quality at the same bitrate.
Difference in visual quality can be easily seen by eye as it’s illustrated on figures 11 and 12:


Turing GPUs come equipped with powerful NVENC video encoding units which delivers higher video compression efficiency compared to sophisticated software encoders like libx264, due to the combination of higher performance and lower energy consumption. The ideal solution for transcoding needs to be cost effective (dollars/stream) and power efficient (watts/stream). Let’s look at performance and power consumption results averaged across multiple test sequences, as presented by figures 13 and 14.
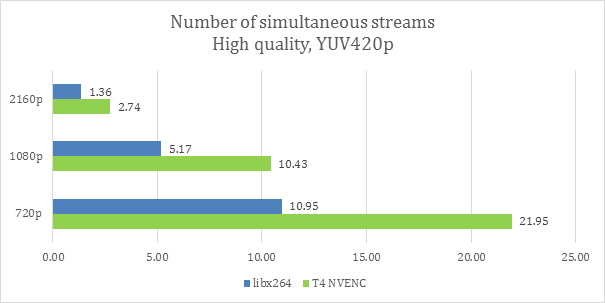
The T4 encodes 22 720p streams, simultaneously in High Quality mode. The GPU can also handle ten streams on average at 1080p and two or three at UltraHD (2160p) resolutions. This equates to almost double that of libx264 at equal visual quality level.
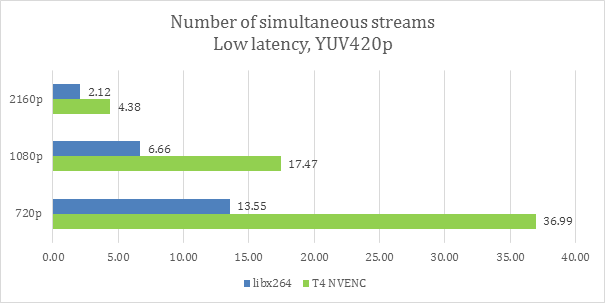
Running in low-latency mode shows an even larger advantage for the T4. It can encode 37 streams at 720p resolution, 17-18 in 1080p, and 4-5 streams in Ultra HD, which is 2-2.7x higher performance than libx264 with higher visual quality. You can see watts per stream charts in figures 15 and 16.
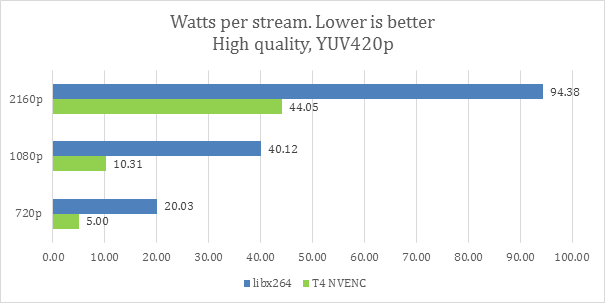

The Tesla also shows great power efficiency, outperforming libx264 2-4x in High Quality mode and up to 5x in Low Latency mode while keeping the CPU load low.
Conclusion
NVIDIA’s Tesla T4 has greatly improved encoding capabilities in comparison to previous generations. It shows the same or better visual quality compared to software encoders like libx264 in High Quality mode while outperforming them in Low Latency mode. This equates to twice the performance at 2-5x lower power consumption.









