NvLogging#
NvLog is the SOC logging solution for NVIDIA DriveOS™. NvLog triages and debugs in-field failures. This feature is supported for all build variants of AV + L. The following section explains the high-level architecture of NvLog.
High Level Architecture#
Early Boot Logging Framework#
SOC Logging is enabled for the following logging entities:
MB1
MB2
SC7rf
MB2rf
ATF
BPMP-FW
PSC-FW
HPSE-FW
SB-FW
MB1 detects errors reported by the previous entities and passes the information to the MCU by communicating over the SPI interface.
Log Types#
MB1 passes two types of code and logs to MCU:
Progress codes: These are the codes to denote the failure entity and the task during which the error occurred.
Error codes: These are the codes to denote the failure reason.
Reset Reason and Reset Level
Log Format#
Each error log line reported on the MCU will consist of three parts:
ReportID
Error_Attribute
Error_Code
Details on how to format them are given below
ReportID#
ReportID should be 0x8141 denoting errors are reported by MB1.
Error_Attribute#
Error_Attribute[0:7] is used to denote type of the code
Code |
Description |
|---|---|
0x01 |
to denote error code |
0x02 |
to denote progress code |
Error_Attribute[8:15] is used to denote origin of the code
Code |
Value |
|---|---|
MB1 |
0x1U |
MB2 |
0x2U |
SC7RF |
0x4U |
MB2RF |
0x8U |
BPMPFW |
0x10U |
ATF |
0x20U |
PSCFW |
0x40U |
HPSE |
0x80U |
SB |
0x100U |
Error_Code (when origin is MB1, MB2, SC7rf or MB2rf)#
Error_Code has different bits allocated depending on the Error_Attribute value.
When the Error_Attribute has type as error code, following format is applied:
Error_Code[0:7] is used to denote the error code reason.
Error_Code[8:15] is used to denote auxiliary information for pinpointing the failure condition during debug.
Error_Code[16:23] is used to denote the lowest caller module.
Error_Code[24:31] is used to denote the highest caller module.
When the Error_Attribute has type as progress code, following format is applied:
Error_Code[0:23] is used to denote the progress code
Error_Code[24:31] is used to denote the origin of the progress code
Runtime Logging Framework#
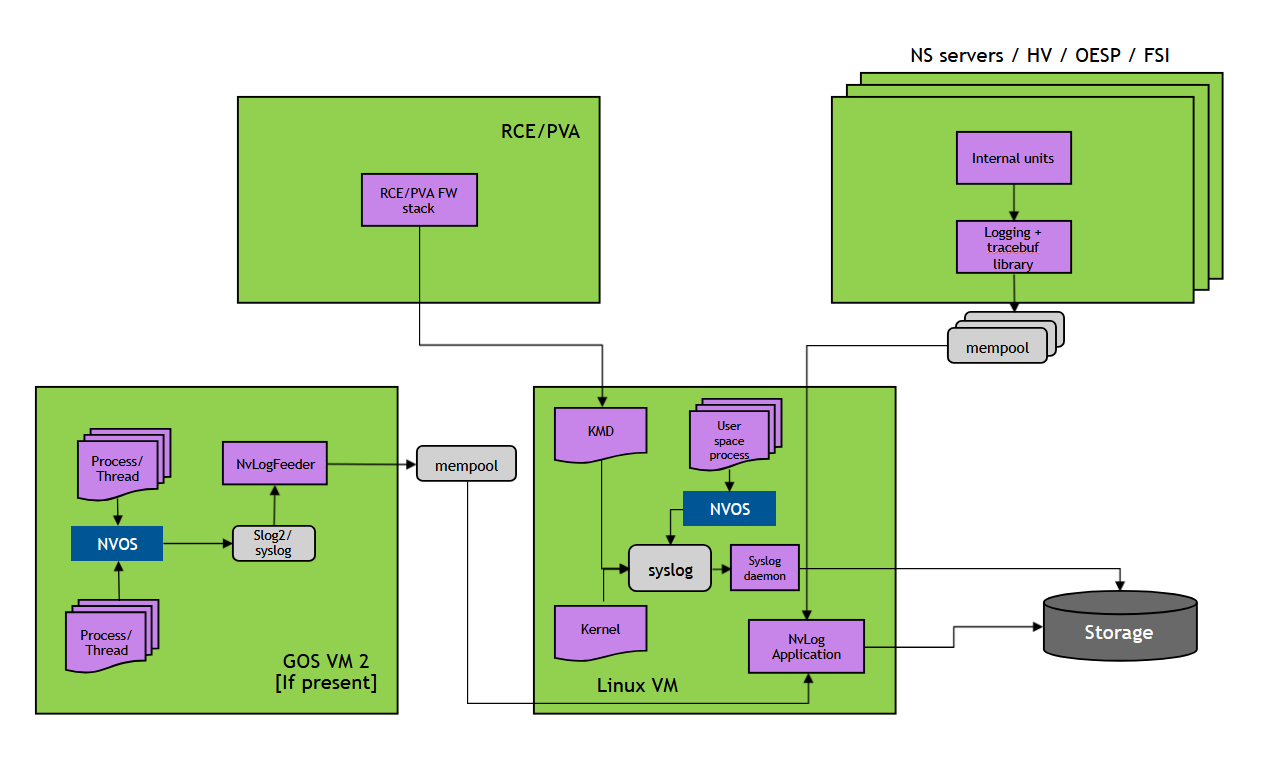
SOC Logging is enabled for the following Logging Entities:
Applications / libraries in GOS0
Linux kernel
Virtualization servers – BPMP server, Storage server, Ethernet server, SE server, NvHost server, Audio server (if enabled), DRIVE Update server, PCIe server, Display server
Hypervisor kernel (EL2)
Trusted Applications (TAs) on HPSE
Auxiliary processors such as RCE, PVA, FSI, DCE
Log Types#
To avoid system-wide KPI impact due to heavy logging, in DriveOS 7.0, only following types of messages are logged by all Logging Entities:
INFO messages at important checkpoints during init
ERROR messages at run time
Log Format#
The logs are stored in custom Nvidia format. A sample log will look as follows:
TIMESTAMP | ENTITY_ID | PID | TID | TYPE | LEVEL | MSG
145318740 500 8 0 0 1 [SS_UFS]: VSC NvLog is Enabled
7476300256 0 737425 1 0 2 [TS=2488520317] MsgReceive ...
2494704578 0 101581 1 0 2 Test CNT = 0
TIMESTAMP : Timestamp of a log message
ENTITY_ID : Logging entity ID in hexadecimal after removing NVLOG_EID_MARK
PID : Process ID
TID : Thread ID
TYPE : Type of a log message (NVLOG_MSG_TYPE_STRING is only supported now)
LEVEL : Verbosity level of a log message
MSG : Payload of a log message
Loging entity IDs are as below.
#define NVLOG_EID_MARK (0xC000U)
/**
* @details Entity IDs for NvLog
* [15:14] EID Mark
* [13:8] Entity ID
* [7:0] Entity specific sub ID, if necessary
*/
/** @details Entity ID of GOS0 VM (The primary Guest VM) */
#define NVLOG_ENTITY_ID_GOS0_VM (NVLOG_EID_MARK)
/** @details Entity ID of DU VM (Update VM) */
#define NVLOG_ENTITY_ID_DU_VM (NVLOG_EID_MARK | 0x0100U)
/** @details Entity ID of GOS1 VM (The secondary Guest VM */
#define NVLOG_ENTITY_ID_GOS1_VM (NVLOG_EID_MARK | 0x0200U)
For consistency in timestamp of logs, NvLog uses TSC (Tegra System Counter) counter value as a timestamp of each log.
The NvLog output file has two cases of logs:
Case 1: Log containing a timestamp token of “[TS:nnnnnn]”
This is the case where logging entity logs original timestamp using this token.
When client applications, which are running on Linux based VM, use NvOS_S3 logging APIs, NvOS_S3 logging API adds a timestamp token of “[TS:nnnnnn]”, where <nnnnnn> means TSC counter value, at the beginning of a log message.
External FW such as PVA, RCE, FSI will also add a token: “[TS:nnnnnn]” at the beginning of the log message.
Case 2: Log not containing a timestamp token
TSC counter value is displayed in the “TIMESTAMP” column.
The post-processing script will pick the correct timestamp value.
Logging by Different Logging Entities#
Logging Entities store their logs in dedicated memory buffers:
Applications in GOS0 and Linux kernel logs – these logs are stored in /mnt/nvlog_logs/gos_logs.txt
FSI FW, Hypervisor kernel, Virtualization servers and secure world TAs – logs are stored in a memory buffer dedicated for each Logging Entity. The logs for these are stored in /mnt/nvlog_logs/nvlog_mgr_out.txt
RCE, PVA – logs are sent to client driver running on CCPLEX and then routed to NvLogMgr via /var/log/syslog buffers.
The NvLogMgr (NvLog server) running in GOS0 periodically wakes up and snoops all shared memory buffers. If there are new logs found in the buffers, it will fetch those logs and store them in the logfile. All these buffers are circular buffers. If the buffer is full, then for storing new logs, earlier logs in the buffer will be overwritten.
Log Collection#
The logs from all the Logging Entities are collected in a logfile.
The logfile is stored in a filesystem on a secondary storage device.
Logs are stored along with a timestamp counter.
The logs are fetched from target and sorted based on timestamp using a post-processing script offline on the host.
Sorted logs can then be analyzed further for debugging.
The system logfile size limit can be configured in device tree. Once the limit is reached, it will wrap around and start writing the logs from the beginning.
For configuration of GOS logfile size on Linux, please update the syslogd config file named: 30-nvlog-vm.conf present in /etc/rsyslog.d/ directory.
Logging Statistics#
The following statistics are displayed by NvLog and updated periodically:
NvLog stores the following statistic of logging in /tmp/ nvlog_statistic.txt.
Total number of logs written to a NvLog output file
Total bytes of logs written to a NvLog output file
Number of messages written per second
Length of messages written per second
Configuration Parameters#
Configuration parameters in device tree and PCT control configuration settings for NvLog.
Note
These configuration parameters apply only to the runtime logging framework; they do not apply to Early Boot Logging. The following table lists these parameters:
Parameters for Syslogd#
Parameters for Guest OS Logging using rsyslog#
Parameter |
Purpose |
Location |
|---|---|---|
type |
Specifies that this action writes log messages to a file. |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
file |
Sets the destination file for log output (/m nt/nvlog_logs/gos_logs.txt) |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
queue.type |
Configures the queue to use disk-based storage for buffering messages. Currently, disk assissted queueing is being used |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
queue.filename |
Sets the base name for the disk queue files (not the directory). |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
queue.spoolDirectory |
Sets the directory where disk queue files are stored (“/var/spool/rsyslog”) |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
queue.maxDiskSpace |
Limits the total disk space used by all queue files to 20 megabytes. |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
queue.maxFileSize= |
Limits each individual queue file to a maximum size of 1 megabyte. |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
queue.dequeueBatchSize |
Sets the maximum number of messages to dequeue from the queue in one batch. |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
queue.minDequeueBatchSize |
Sets the minimum number of messages to dequeue in a batch, waiting if necessary. Currently set to 2048 |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
queue. minDequeueBatchSize.timeout |
Waits up to 5000 milliseconds to reach the minimum batch size before dequeuing. |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
queue.saveOnShutdown |
Ensures unsent messages in the queue are saved to disk on shutdown. Currently set to “on” |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
rotation.sizeLimit= |
Triggers a rotation event when the output file reaches 10 megabytes. |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
rotation.sizeLimitCommand |
“/usr/ local/bin/clear_goslog.sh”: Runs the specified script when the file size limit is reached. |
30-nvlog -vm.conf |
Rsyslog is an open-source utility provided in Linux for logging. The
file 30-nvlog-vm.conf is a custom configuration file for guest OS
logging. Rsyslog configuration doesn’t take information from external
files, hence taking values from the device-tree. For further information
and details on each parameter and rsyslog behaviour, please refer to its
official documentation.
Control Knobs to Enable and Disable Logging for Entities#
Additional control knobs in PCT enable and disable logging for a specific logging entity and set the logging buffer size.
Parameter |
Purpose |
Location |
|---|---|---|
bpmp_server_native_conf.nvlog_buff_size |
Logging buffer allocated to BPMP server. If set to zero, logging from BPMP server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
se_server_native_conf.nvlog_buff_size |
Logging buffer allocated to SE server. If set to zero, logging from SE server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
ethernet_server_native_conf.nvlog_buff_size |
Logging buffer allocated to Ethernet server. If set to zero, logging from Ethernet server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
vsc_server_native_ufs_conf.nvlog_buff_size |
Logging buffer allocated to UFS storage server. If set to zero, logging from UFS server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
vsc_server_native_sdmmc_conf.nvlog_buff_size |
Logging buffer allocated to SDMMC storage server. If set to zero, logging from SDMMC server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
vsc_server_native_qspi_conf.nvlog_buff_size |
Logging buffer allocated to QSPI storage server. If set to zero, logging from QSPI server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
audio_server_native_conf.nvlog_buff_size |
Logging buffer allocated to Audio server. If set to zero, logging from Audio server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
Vm_server_conf.nvlog_buf_size |
Logging buffer allocated to nvhost server. If set to zero, logging from nvhost server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
du_server_conf.nvlog_buf_size |
Logging buffer allocated to DU server. If set to zero, logging from DRIVE Update server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
pcie_server_native_conf.nvlog_buff_size |
Logging buffer allocated to PCIe server. If set to zero, logging from PCIe server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
display_server_conf.nvlog_buff_size |
Logging buffer allocated to display server. If set to zero, logging from display server will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
platform_conf.nvlog_size |
Logging buffer allocated to HV kernel. If set to zero, logging from HV kernel will be disabled. |
PCT (platform_config.h) |
Note
For Virtualization servers, the buffer size mentioned in the PCT is divided equally among all the threads/LCPUs.
The minimum required buffer size is 0x4520 bytes per thread.
Execution Steps#
Early Boot Logging Framework#
To enable Boot Logging Framework, set the enable_early_error_reporting field in the MB1-BCT dtsi file located at:
${NV_WORKSPACE}/hardware/nvidia/platform/t264/automotive/bct/<BOARD_TYPE>/misc/tegra264-mb1-bct-misc-<board_type>.dts
This field will be set to <1> by default, denoting that the framework is enabled. To disable the framework, this field should be set to <0>.
Runtime Logging Framework#
On boot, NvLog logfile is created at: /mnt/nvlog_logs. There will be the following logfiles under this path:
System log file for previous boot is retained as: “nvlog_mgr_out.txt.old”
System log file for current boot cycle is stored as: “nvlog_mgr_out.txt”
GOS log file for current boot cycle stored as: “gos_logs.txt”
GOS log file for previous boot cycle stored as: “gos_logs.txt”/mnt/nvlog_logs/gos_logs.txt.old
Step 1#
The NvLog feature is enabled by default for AV + L on all platforms. The logfiles will be created at: “/mnt/nvlog_logs/”.
Disable NvLog#
To disable NvLog server, make following change in device tree:
For linux, please refer: common/linux/tegra264-linux-nvlog.dtsi
diff --git a/common/linux/tegra264-linux-nvlog.dtsi
b/common/linux/tegra264-linux-nvlog.dtsi
index 129a483..300a51d 100644
--- a/common/linux/tegra264-linux-nvlog.dtsi
+++ b/common/linux/tegra264-linux-nvlog.dtsi
@@ -529,7 +529,7 @@
};
nvlog {
- status = "okay";
+ status = "disabled";
Disable logging by syslogd: Logging by syslogd into a separate text file (gos_logs.txt) can be disabled by removing the corresponding conf file 30-nvlog-vm.conf located in /etc/rsyslog.d/
Recompile and flash.
Step 2#
Copy the nvlog files and run post-processing script as follows:
python3 drive-linux/samples/tools/nvlog/scripts/host/systemlog_parser.py
-in gos_logs.txt nvlog_mgr_out.txt -out output.txt -add*
The script will merge two logfiles into one and generate an output file which will contain logs ordered based on timestamps.
Integration with Customer Applications#
Runtime Logging from customer applications can be integrated with NvLog by linking with NvOS library.
NvOS logging APIs are found in ${SDK\_INCLUDE\_DIR
}/nvos\_s3\_tegra\_log.h.
Assumptions, Restrictions and Recommendations (ARRs)#
RES-001: Always log only errors at run time#
NvLog framework currently does not support rate limiting. So, if a Logging Entity sends logs in large volume, it could impact system-level KPIs. To avoid this, Logging Entity is required to send only error logs to NvLog.
RES-002: Avoid repetitive logging#
To avoid continuous flood of logs, avoid repetitive logging from any logging entity.